The role of Zn-complexing agents in the chemical bath deposition of ZnO and ZnS thin films
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47566/2022_syv35_1-221202Keywords:
Thermodynamic analysis, Equilibrium chemical, ZnS, Thin films deposition, Complexing agentsAbstract
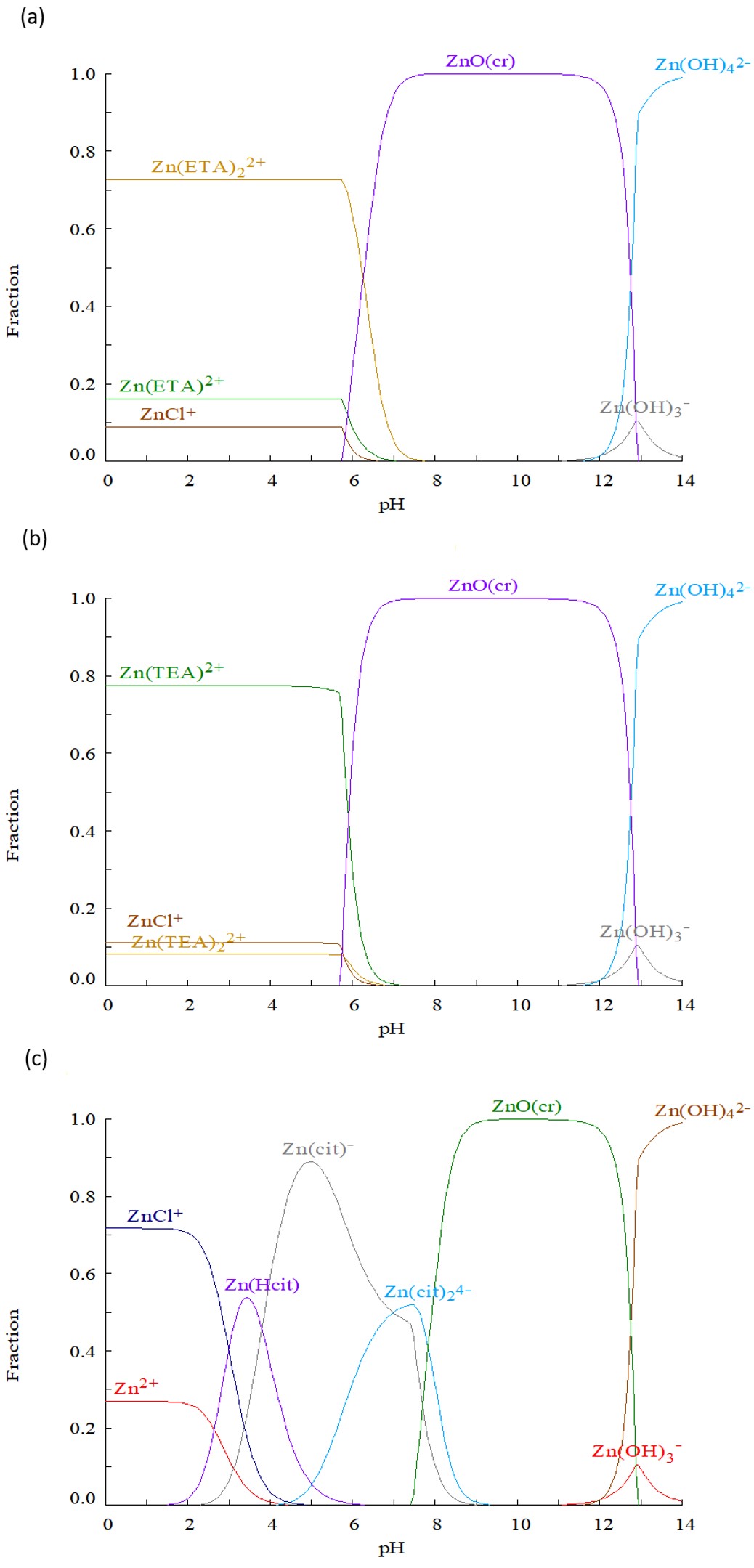
In order to control the deposition of Zn-related films by chemical bath deposition, the effects of Zn-complexing agent are analyzed. ZnS films were produced by chemical bath deposition technique employing sodium citrate, ethanolamine and Triethanolamine as complexing agents. The deposition conditions for ZnS (ZnO) thin films were obtained through a thermodynamic analysis, using distribution diagrams for molar fraction of Zn complexes. From species distribution diagrams of Zn-ethanolamine, Zn-Triethanolamine and Zn-citrate. It was found that for pH values between 4 and 6 the highest Zn fraction is obtained. The results highlight the importance of complexing agent morphology, while the use of ethanolamine and triethanolamine produce ZnO films due to their high reactivity; the use of sodium citrate produce ZnS films. Deposited ZnS films have a cubic structure, n-type conductivity, resistivity of 8.36×104 ??cm with a 3.75 eV bandgap.
References
.[1]. S. Chen, R. Yu, L. Song, R. Zhang, X. Cao, B. Wang, P. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 498, 143876 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143876
.[2]. P.A. Ajibade, A.E. Oluwalana, B.M. Sikakane, M. Singh, Chem. Phys. Lett. 755, 137813 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137813
.[3]. D. Agrawal, S.L. Patel, Himanshu, S. Chander, M.S. Dhaka, Opt. Mater. 105, 109899 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109899
.[4]. B. Deng, Y. Zhu, J. Li, X. Chen, K. He, J. Yang, K. Qin, Z. Bi, X. Xia, S. Chen, X. Xu, G. Xu, J. Alloys Compd. 845, 155400 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155400
.[5]. S.N. Sadikin, M.Y.A. Rahman, A.A. Umar, Optik 211, 164644 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164644
.[6]. Y. Ye, L. Wang, K. Liu, J. Li, Microchem. J. 155, 104749 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104749
.[7]. F. Zhang, H. Wang, X. Zhou, Y. Zhao, J. Duan, Opt. Laser Technol. 127, 106145 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106145
.[8]. J.M. Jacob, R. Rajan, T.C. Tom, V.S. Kumar, G.G. Kurup, R. Shanmuganathan, A. Pugazhendhi, Ceram. Int. 45, 24193 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.128
.[9]. H. Qin, T. Hu, Y. Zhai, N. Lu, J. Aliyeva, J. Hazar. Mater. 400, 123161 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123161
.[10]. O. Toma, L. Ion, S. Iftimie, V.A. Antohe, A. Radu, A.M. Raduta, D. Manica, S. Antohe, Appl. Surf. Sci. 478, 831 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.032
.[11]. K. Benyahia, A. Benhaya, M.S. Aida, J. Semicond. 36, 103001 (2015).
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/2013/T157/014043
.[12]. K. Yang, B. Li, G. Zeng, Superlattices Microstruct. 130, 409 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2019.05.009
.[13]. K. Ghezali, L. Mentar, B. Boudine, A. Azizi, J. Electroanal. Chem. 794, 212 (2017).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.04.030
.[14]. D. Chiu, Y. He, Z. Gao, C. Remple, C.-H. Chang, ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 7, P615 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0031811jss
.[15]. Y. Zhu, Y. Zhang, L. Yan, D. Zhang, J. Zhou, S. Adimi, S. Ruan, J. Alloys Compd. 832, 155022 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155022
.[16]. M. Sathishkumara, M. Saroja, M. Venkatachalam, Optik 182, 774 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.02.014
.[17]. N. Kumar, L.P. Purohit, Y.C. Goswami, Physica E 83, 333 (2016).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2016.04.025
.[18]. G. Arandhara, J. Bora, P.K. Saikia, Mater. Chem. Phys. 241, 122277 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122277
.[19]. R.P. Khatri, A.J. Patel, IJRASET 6, 1705 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2018.3263
.[20]. C. Ekberg, P.L. Brown. Hydrolysis of Metal Ions (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, 2016).
https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527656189
.[21]. Z-Y Ding, Q-Y Chen, Z-L Yin, K. Liu, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23, 832 (2013).
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62536-4
.[22]. L.A. Kochergina, A.V. Volkov, D.V. Krutov, O.N. Krutova, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 80, 899 (2006).
https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024406060100
.[23]. H. Kazimierczak, P. Ozga, R.P. Socha, Electrochim. Acta 104, 378 (2013).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.12.140
.[24]. A. Goux, T. Pauporté, J. Chivot, D. Lincot, Electrochim. Acta 50, 2239 (2005).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2004.10.007
.[25]. G. Hodes, Chemical solution deposition of semiconductor films (Marcel Dekker Inc, 2002).
https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203909096
.[26]. I.J. González-Panzo, P.E. Martín-Várguez, A.I. Oliva, J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, D181 (2014).
https://doi.org/10.1149/2.067404jes
.[27]. T.V. Vinogradova, V.F. Markov, L.N. Maskaeva, Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 80, 2341 (2010).
https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363210110198
.[28]. S.J. Ashcroft, J. Chem. Eng. Data 33, 73 (1988).
https://doi.org/10.1021/je00052a001
.[29]. A. Nasar, M. Shamsuddin, Thermochim. Acta 205, 157 (1992).
https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(92)85257-V
.[30]. G. Eriksson, Anal. Chim. Acta 112, 375 (1979).
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)85035-2
.[31]. D.W. Ball, Physical Chemistry, 2nd Ed. (Cengage Learning, 2014).
https://www.cengagebrain.com.mx/shop/isbn/9781133958437
.[32]. I.J. González-Chan, A.I. Oliva, J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, D421 (2016).
https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0911608jes
.[33]. A. Karimi, B. Sohrabi, M.R. Vaezi, Thin Solid Films 651, 97 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2018.02.021
.[34]. A. Wei, J. Liu, M. Zhuang, Y. Zhao, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1478 (2013).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2013.03.016
.[35]. N. Prasad, B. Karthikeyan, Nanotechnology 30, 485702 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab3cbf
.[36]. S-J Young, C-C Yang, L-T Lai, J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, B3013 (2017).
https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0051705jes
.[37]. J Theerthagiri, S. Salla, R.A. Senthil, P Nithyadharseni, A. Madankumar, P. Arunachalam, T. Maiyalagan, H-S Kim, Nanotechnology 30, 392001 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab268a
.[38]. Z. Mao, C. Fu, X. Pan, X. Chen, H. He, W. Wang, Y. Zeng, Z. Ye, Phys. Lett. A 384, 126148 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2019.126148
.[39]. D. Himmel, L.C. Maurin, O. Gros, J-L Mansot, Biol. Cell 101, 43 (2009).
https://doi.org/10.1042/BC20080051
.[40]. Z. Li, M. Chen, Q. Zhang, J. Qu, Z. Ai, Y. Li, Appl. Clay Sci. 144, 115 (2017).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.05.015
.[41]. C.M. Samba Vall, M. Chaik, H. Ait Dads, H. El Aakib, M. Elyaagoubi, M. Aggour, A. Outzourhit, J. Semicond. 39, 123001 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/39/12/123001
.[42]. F. Zakerian, H. Kafashan, Superlattices Microstruct. 124, 92 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2018.09.039
.[43]. A.E. Igweoko, C. Augustine, N.E. Idenyi, B.A. Okorie, F.N.C. Anyaegbunam, Mater. Res. Express 5, 036413 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aab652
.[44]. W. Zhang, X. Zeng, J. Lu, H. Chen, Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 3843 (2013).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.084
.[45]. A. Goktas, F. Aslan, E. Yasar, I.H. Mutlu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23, 1361 (2012).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0599-z
.[46]. S. Gallanti, E. Chassaing, D. Lincot, N. Naghav, Electrochim. Acta 178, 225 (2015).
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The authors; licensee SMCTSM, Mexico.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
©2025 by the authors; licensee SMCTSM, Mexico. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





