Method for measuring the setting process of cement-water mixtures by electrical impedance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47566/2024_syv37_1-240101Keywords:
Electrical resistivity, electrical impedance, hydration, cement, setting timeAbstract
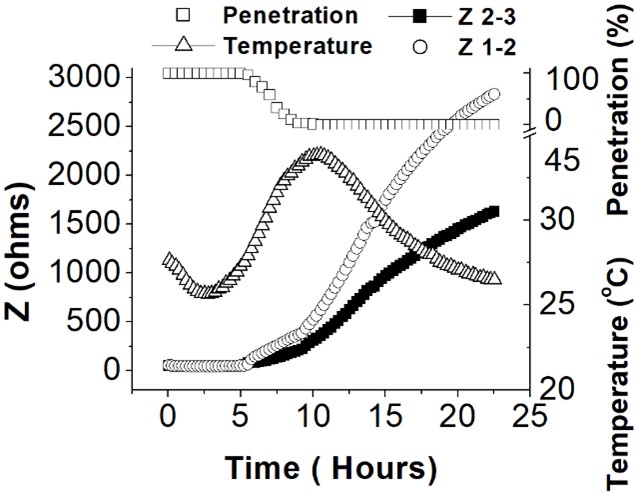
The setting and hardening of cement paste can be taken as the progressive hydration reaction of cement. This paper reports the findings on setting time of cement paste at early hydration by using a novel method named relative electrical impedance (REI). The novel REI method measures the relative electrical impedance between electrodes (ring shaped) embedded in the cement paste. REI measurements were conducted on cement paste samples with a water-cement ratio of 1:2 over 24 hours. REI measurements were compared with VICAT and heat latent methods for indirect validation. It was found that the proposed REI technique determined the 4 periods of the setting time process (sleeping, hydration, deceleration, and diffusion) and allowed the measurement of the sleeping period in detail. It was concluded that the novel REI method could be used as a new method to measure the setting time of cement paste in early hydration.
References
. P.H. Jézéquel, V. Collin, Cem. Concr. Res. 37, 1321 (2007).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.05.007
. A. Emanuelson, S. Hansen, E. Viggh, Cem. Concr. Res. 33, 1613 (2003).
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(03)00115-7
. K. Scrivener, A. Nonat, Cem. Concr. Res. 7, 651 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.03.026
. M. Michaux, E.B. Nelson, B. Vidick, Developments in Petroleum Science 28, 2-1-2-17 (1990).
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7361(09)70300-0
. A. Smith, P. Abélard, F. Thummen, A. Allemand, Cem. Concr. Compos. 24, 477 (2002).
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(01)00079-8
. J. Pineda, J. Vega, A. Manzano, E. Prokhorov, E. Morales, J. González, Appl. Clay Sci. 40, 1 (2008).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2007.06.006
. M.R. Moreno-Virgen, J.J. Soto-Bernal, J.A. Ortiz-Lozano, A. Bonilla-Petriciolet, J.T. Vega-Durán, R. González-Mota, J. Pineda-Piñón, Mater. Construcc. 61, 77 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2010.54709
. M.A. Gabalec, M. Barreda, Tiempo de fraguado del hormigón (Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, Argentina, 2008).
https://es.scribd.com/document/107103750/Tesis2008-Anabela-Gabalec-Tiempo-de-Fraguado-Del-Hormigon
. ASTM C191-99, Standard Test Method for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle (West Conshohocken, PA, USA, ASTM International, 2001).
https://doi.org/10.1520/C0191-99
. R. Ylmen, U. Jäglid, B. Steenari, I. Panas, Cem. Concr. Res. 39, 433 (2009).
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEMCONRES.2009.01.017
. D. Vladikova, J. Kilne, S. Skinner, G. Raikova, Z. Stoynov, Electrochim. Acta 8, 1611 (2006).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.02.110
. D.V. Ribeiro, C.A.D. Rovere, C.A.C. Souza, S.E. Kuri, J.A. Labrincha, J.C.C. Abrantes, M.R. Morelli, Int. Sch. Res. Notices 2011, 11 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/365276
. G. Sant, C. Ferraris, J. Weiss, Cem. Concr. Res. 38, 1286 (2008).
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEMCONRES.2008.06.008
. H. Sleiman, A. Perrot, S. Amziane, Cem. Concr. Res. 40, 681 (2010).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.12.001
. D. Lootens, P. Jousset, L. Martinie, N. Roussel, R. Flatt, Cem. Concr. Res. 39, 401 (2009).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.01.012
. K. Backe, O. Lile, S. Liomov, SPE Drill. Complet. 16, 201 (2001).
https://doi.org/10.2118/74694-PA
. D. Sánchez de Guzmán, Tecnología del concreto y del mortero, 5ª Ed. (Bhandar Editores LTDA, 2001).
https://isbn.cloud/9789589247044/tecnologia-del-concreto-y-del-mortero/
. P.K. Mehta, P.J.M. Monteiro, Concrete Microstructure, Properties, and Materials (McGraw-Hill Education, 2014).
https://www.accessengineeringlibrary.com/content/book/9780071797870
. M. Cabeza, Cem. Concr. Res. 32, 881 (2002).
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)00720-2
. J. Cruz, J. Payá, F. Lalinde, Mater. Construccion. 61, 7 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2010.53709
. L. Xiao, Z. Li, Cem. Concr. Res. 38, 312 (2008).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.09.027
. R. Ylmen, B. Jäglid, I. Steenari, Cem. Concr. Res. 39, 433 (2009).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.01.017
. J. Bullard, H. Jennings, R. Livingston, A. Nonat, G. Scherer, J. Schweitzer, K. Scrivener, J. Thomas, J. Biernacki, Cem. Concr. Res. 41, 1208 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.09.011
. V. Bonavetti, C. Castellanos, H. Donza, V. Rahhal, E. Irassar, Cem. Concr. Res. 5, 40 (2013).
http://dx.doi.org/10.3989/mc.2014.04813
. P. Moses, S. Perumal, IOSR-JMCE 13, 17 (2016).
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors; licensee SMCTSM, Mexico.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
©2025 by the authors; licensee SMCTSM, Mexico. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





